HOW CAN EMR IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF CARE IN HEALTHCARE?
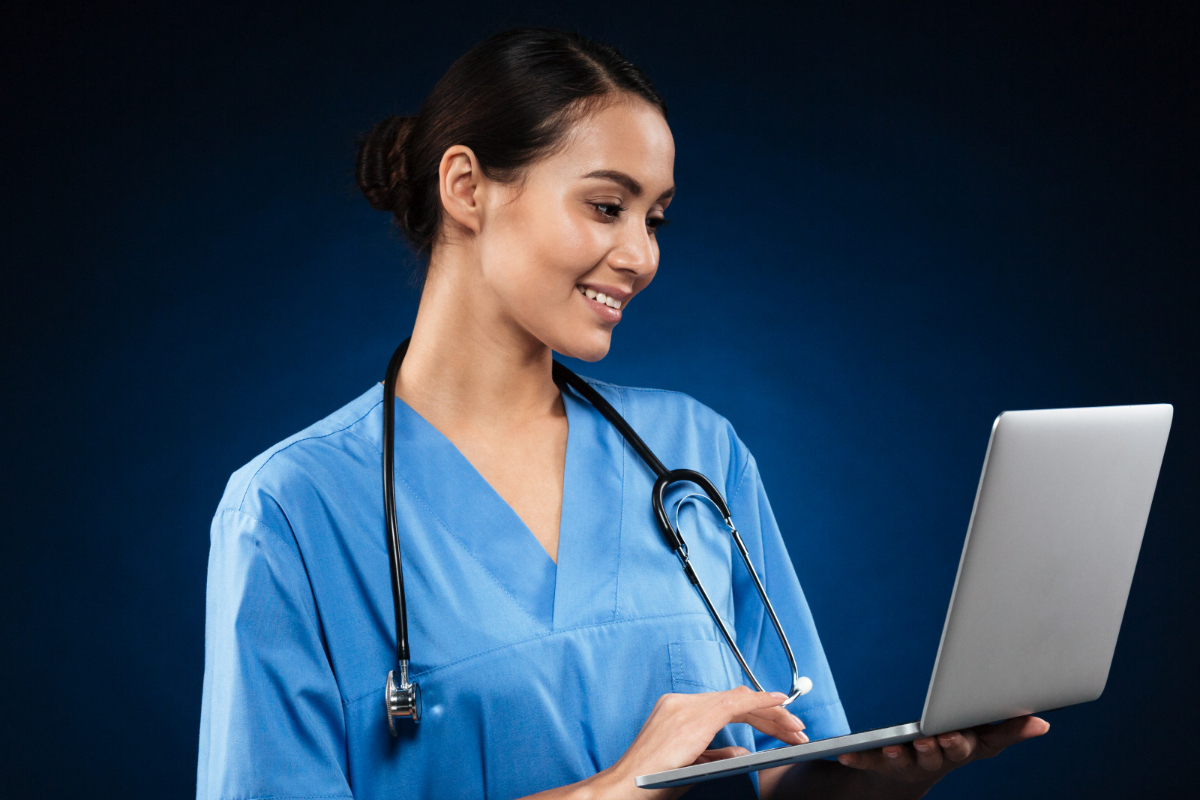
Electronic medical records improve quality of care, patient outcomes, and safety through improved management, reduction in medication errors, reduction in unnecessary investigations, and improved communication and interactions among primary care providers, patients, and other providers involved in care.
What is Electronic Medical Records(EMR)?
An electronic medical record (EMR) is a digital version of all the information found in a provider’s paper chart, including medical history, diagnosis, medications, immunization dates, allergies, lab results, and doctor’s notes. EMRs are online medical records that contain standard medical and clinical data from a single provider’s office and are mostly used for diagnosis and treatment by providers. In EMRs, complete and accurate documentation of a patient’s medical history, tests, diagnosis, and treatment ensures that appropriate care is provided throughout the provider’s clinic.
EMRs are more than just a paper record replacement. They enable effective communication and coordination among members of a healthcare team in order to provide the best possible care to patients.
Electronic Medical Records(EMRs) are a digital version of the charts in the clinician’s office. An EMR contains the medical and treatment.
An electronic (digital) collection of a person’s medical information stored on a computer. Diagnosis, medications, tests, allergies, immunizations, and treatment plans are all part of a patient’s electronic medical record.
The Institute of Medicine(IOM) 2003 Patient Records Describes an EMR as encompassing:
- “A longitudinal collection of electronic health information for and about persons.
- Immediate electronic access to person and population-level information by authorized users.
- Provision of knowledge and decision-support systems that enhance the quality, safety, and efficiency of patient care.
- Support for efficiency processes for health care delivery.”
Importance quality care in healthcare.
Health care quality is defined by the Institute of Medicine as “the extent to which health care services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes and are consistent with current professional knowledge.”
Quality control is the process of testing a sample of manufactured goods to ensure it meets standard specifications. Quality control is critical in the medical industry because the equipment produced is used for medical purposes.
Quality healthcare is critical for all providers, patients, and their families. The Institute of Medicine( IOM) has identified six critical domains of healthcare quality: patient safety, effectiveness, patient-centeredness, timeliness, efficiency, and equity:
- Patient Security:
Patient safety is the principle that ensures people receiving healthcare services are treated with dignity and respect. Patients must be able to put their trust in the healthcare system to receive safe, high-quality care.
- Efficiency:
The effectiveness of a healthcare service refers to how well it achieves its intended purpose. Effective services are more likely to be safe and to provide patients with the desired benefits.
- Patient-centered:
Patient-centered care is a philosophy and approach to health care that emphasizes the importance of the patient’s perspective. It involves working with patients to identify their needs and ensuring that their concerns are taken into account when planning and delivering health services.
- Reliability:
To put it simply, timely care means providing health services as soon as possible. This is especially true for emergency services, which must be available whenever and wherever they are required.
Patients can suffer serious consequences if care is delayed. Delays in diagnosing a serious illness, for example, can result in severe complications or even death. Furthermore, delayed treatments can result in serious harm or even death.
- Equity:
Healthcare systems should be equitable, which means that no one group of people should receive better or worse care than another. Everyone in society should have access to appropriate healthcare, regardless of age, gender, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, physical ability, geographic location, or other factors.
- Effectiveness:
Efficiency is a measure of how well a company uses its resources to generate output. It can be examined in terms of inputs (such as financial and human resources), outputs (such as services provided), and processes (e.g., management). Efforts to increase efficiency frequently seek ways to cut unnecessary costs or increase output while maintaining or improving quality standards.
How EMR can help in so…
The EMR allows clinicians to see more patients by improving access to comprehensive patient histories that include clinical data, potentially saving physicians time searching for results and reports.
More Benefits of using EMR
EMR Benefits for Patients:
- Fewer errors in medical records.
- Medical professionals can assess and care for patients more quickly.
- Data and outcomes are tracked over time.
- Improved health diagnosis, treatment, and overall care quality
- Identify patients who are due for preventive visits and screenings.
- Increased patient data privacy and security.
- Patient errors are reduced, and patient care is improved.
- Allow for evidence-based decisions to be made at the point of care.
- After-visit information such as self-care instructions, reminders for other follow-up care, and links to web resources.
- Access to the patient’s own records to view medications and keep track of lifestyle changes that have improved their health.
EMR Benefits for Clinics:
- Save space by eliminating the need to store, manage, and retrieve paper records.
- Increase the number of patients served per day by optimizing workflow.
- Reduce administrative burdens and operational expenses.
- Easily communicate with hospitals, pharmacies, labs, and state health systems.
- Electronic records that can be customized and scaled.
- Collect and analyze patient data to enable outreach to specific populations.
- Send out clinical alerts and reminders.
- Enhance the documentation and coding.
- Improve clinical quality through research and monitoring.
- Provide built-in safeguards against prescribing treatments that are likely to cause adverse events.
- Monitor electronic messages sent to staff, other clinicians, hospitals, labs, and so on.
- Public health systems, such as registries and communicable disease databases, are linked.
How Simbo.AI can help:
Simbo is an artificial intelligence-powered bot designed to assist junior doctors. It meets with patients to understand their complaints, records vitals and presents a summary to the doctor, listens to and understands doctor-patient conversations, takes doctor instructions, and then generates an EMR for them. The technology used is called Brain-Inspired Spoken Language Understanding (BISLU).