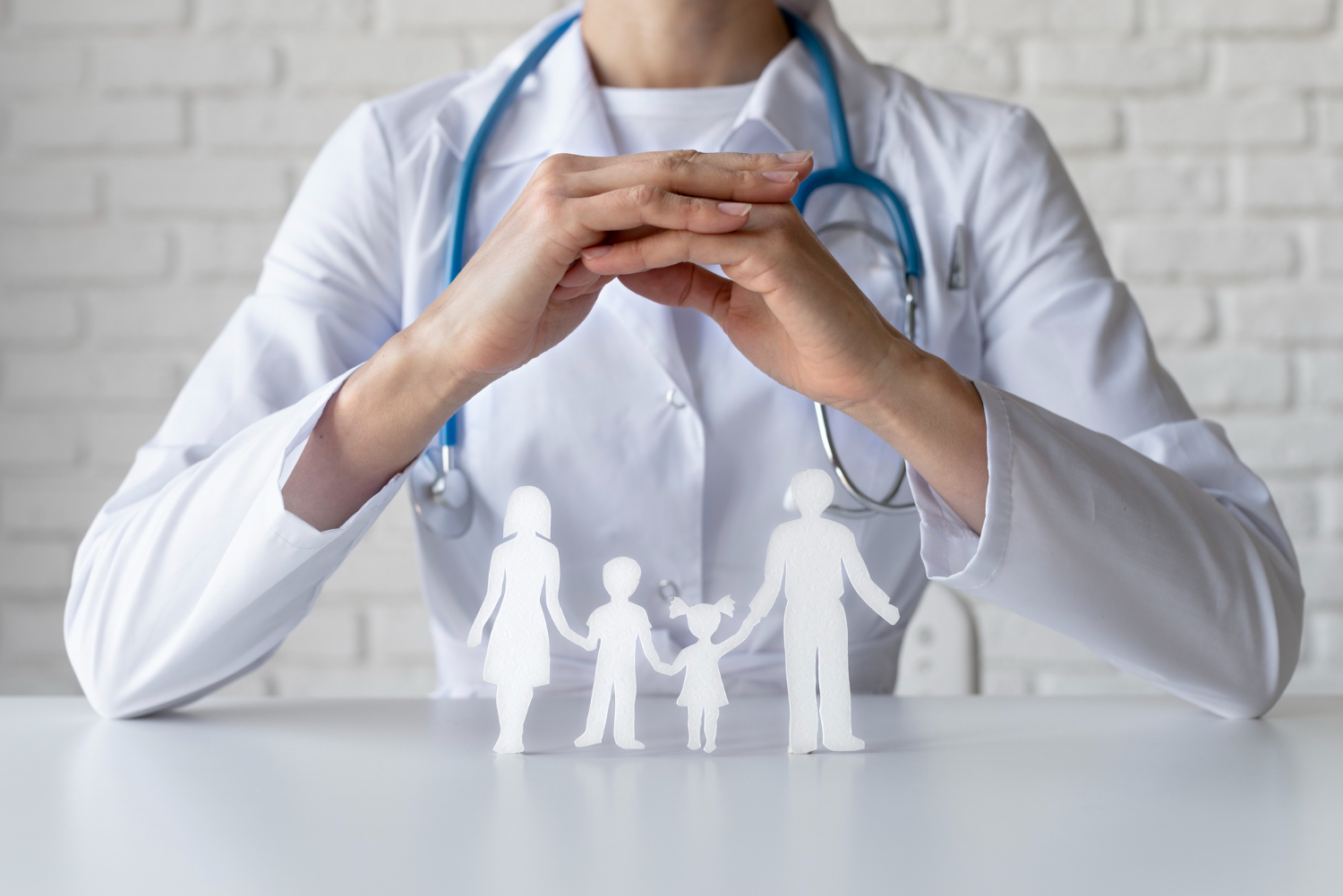
Balancing innovation and patient privacy in U.S. healthcare is essential for advancing medical breakthroughs while protecting individual rights. Striking this balance involves robust privacy regulations like HIPAA, which safeguard patient information. Healthcare organizations must invest in secure data handling technologies and establish clear consent processes to ensure patients’ confidential data is respected. Ethical considerations and data anonymization practices play a pivotal role in maintaining trust while fostering innovation. Ultimately, the United States aims to harness innovation as a force for improved healthcare outcomes while upholding stringent privacy standards.
The Value of Innovation in Healthcare:
Innovation in healthcare stands as a beacon of hope and progress in a rapidly evolving world. Its intrinsic value cannot be overstated, as it is a catalyst for improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and enhancing overall healthcare delivery.
First and foremost, innovation has the potential to transform patient care. Breakthroughs in medical technology, pharmaceuticals, and treatment modalities empower healthcare professionals to diagnose diseases earlier, customize therapies to individual needs, and even cure previously incurable conditions. This translates into improved patient well-being, reduced suffering, and an extended life expectancy.
Furthermore, innovation has a profound impact on cost-effectiveness. Streamlining administrative processes, optimizing resource allocation, and implementing telehealth solutions can significantly cut healthcare expenditures. This makes quality care more accessible and affordable, easing the financial burden on individuals and healthcare systems alike.
In addition, innovation fosters collaboration among healthcare stakeholders. It encourages cross-disciplinary approaches, knowledge sharing, and the development of best practices, ultimately leading to more coordinated, patient-centered care.
The value of healthcare innovation extends beyond patient care and financial considerations. It fuels economic growth by creating jobs, nurturing a thriving healthcare industry, and attracting investment. Moreover, it strengthens the resilience of healthcare systems in the face of unforeseen challenges, such as pandemics.
In conclusion, innovation in healthcare is a driving force that enhances patient outcomes, reduces costs, fosters collaboration, and promotes economic growth. Its value transcends boundaries, offering a brighter and healthier future for individuals and societies worldwide.
The Importance of Patient Privacy:
Patient privacy is a fundamental and non-negotiable aspect of healthcare, serving as the fundament of trust, ethical practice, and effective medical care. Its importance cannot be overstated, and here are several reasons why patient privacy is paramount:
1. Trust and Confidence:
Maintaining patient privacy builds trust between healthcare providers and patients. When individuals trust that their personal health information will remain confidential, patients are more likely to share sensitive details about their medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
2. Ethical Responsibility:
Respecting patient privacy is an ethical obligation of healthcare professionals. It upholds the principles of autonomy and individual rights, ensuring that patients have control over who accesses their health information and for what purpose. This respect for autonomy is central to medical ethics.
3. Effective Care:
Patient privacy enables healthcare providers to deliver effective care. Physicians and nurses need access to complete and accurate patient information to make informed decisions, prescribe appropriate treatments, and avoid potential complications. Without privacy safeguards, patients may withhold crucial information out of fear, compromising their care.
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
Many countries have strict laws and regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, that mandate the protection of patient privacy. Healthcare organizations that fail to comply with these laws face severe penalties, including fines and legal consequences.
5. Data Security:
Patient information is highly valuable and sensitive, making it a prime target for cyberattacks and identity theft. Ensuring patient privacy includes safeguarding electronic health records and employing robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches.
6. Psychological Well-being:
Public Health and Research: Protecting patient privacy is essential for conducting medical research and public health initiatives. Researchers can gather valuable data without compromising individual identities, contributing to advancements in healthcare and disease prevention.
In summary, patient privacy is a vital component of healthcare that underpins trust, ethical practice, effective care, and legal compliance. It is essential to respect and protect patient privacy at all levels of the healthcare system to ensure the well-being of individuals and the integrity of the healthcare profession.
Strategies for Balancing Innovation and Privacy:
Balancing innovation and privacy in healthcare is a complex endeavor that requires careful consideration of ethical, legal, and technological factors. Here are some strategies to strike this balance effectively:
1. Clear Privacy Policies and Consent:
Healthcare organizations should establish transparent privacy policies and seek informed consent from patients regarding the use of their data for innovation purposes. Patients should understand how their information will be used and have the option to opt in or out of data-sharing initiatives.
2. Data Anonymization and De-Identification:
Implement robust data anonymization and de-identification techniques to protect patient identities while still allowing for the use of anonymized data in research and innovation. This ensures that personal information remains confidential.
3. Secure Data Storage and Transmission:
Invest in state-of-the-art cybersecurity measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access, breaches, or cyberattacks. Encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are crucial components of data protection.
4. Data Minimization:
Collect only the minimum necessary data for innovation purposes. Avoid over-collection of information that is not directly relevant to research or patient care to minimize privacy risks.
5. Ethical Data Use Committees:
Establish interdisciplinary committees that include medical ethicists, privacy experts, and patient representatives to evaluate and approve projects involving patient data. These committees can assess the ethical implications and potential privacy risks of innovative initiatives.
6. Continuous Staff Training:
Ensure that healthcare staff are well-trained in privacy regulations and best practices. Education and awareness programs can help prevent unintentional breaches and privacy violations.
7. Patient Control and Access:
Empower patients to control their health data by providing access to their records and the ability to manage data-sharing preferences. Patient-controlled platforms can enhance transparency and trust.
8. Selective Data Sharing:
Allow patients to choose which aspects of their data they are comfortable sharing for research or innovation purposes. This empowers patients to be active participants in the decision-making process.
9. Blockchain Technology:
Explore the use of blockchain for secure and transparent data sharing. Blockchain can offer a decentralized and immutable ledger for healthcare data, ensuring transparency and trust in data transactions.
10. Ethical AI and Algorithm Development:
Ensure that AI and algorithms used in healthcare innovation are developed ethically, with fairness and privacy in mind. Regularly assess and address biases in these technologies to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
In summary, balancing innovation and privacy in healthcare is a multifaceted challenge that requires a combination of technology, policy, and ethical considerations. By adopting these strategies and actively involving patients in the decision-making process, healthcare organizations can harness the power of innovation while safeguarding patient privacy.
AI Medical CALLBOTS:
Do you know AI Medical CALLBOTs can help you in answering routine questions of patients in the front-end to assigning tasks to staff at the back-end.
Simbo’s AI-CALLBOT not only interacts with patients and answers all the routine questions in natural conversation about office hours to manage appointment requests in the front-end but also assigns more complex requests to relevant staff in the back-end. It ensures no patient calls are missed, increasing patient satisfaction and hospital revenue. It’s a complete comprehensive end to end call management software. Its multi-lingual, HIPPA complaint and available 24/7.
CLICK → Book a Demo for AI-Powered CALLBOT!
Simbo.AI is on a mission to make data collection and documentation for patients and healthcare practices as simple as possible. Its voice-AI technology makes it easier for patients, billing staff, clinical staff, and, most importantly, providers, to complete their tasks, resulting in lower burnout, more throughput, and more engaged and satisfied patients.
CLICK → AI Medical Scribe Software DEMO!
SimboAlphus is an AI-powered medical scribe that produces documentation for physicians without any effort and can save them up to three hours each day. The artificial intelligence solution enables providers to speak naturally by building on top of speech-to-text. It comprehends speech and divides clinical content into many categories. It collects structured data from speech to assist providers in producing better billing documents.